Electromyography (EMG)
What is an Electromyography (EMG)?
Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic test used to evaluate the health of muscles and the nerves that control them (motor neurons). These nerves transmit electrical signals when they are stimulated by muscle contractions such as bending a leg.
During EMG, needle electrodes are inserted through the skin into muscles to pick up the electrical activity, which is then translated into graphs, sounds, or numerical values for a specialist to interpret.
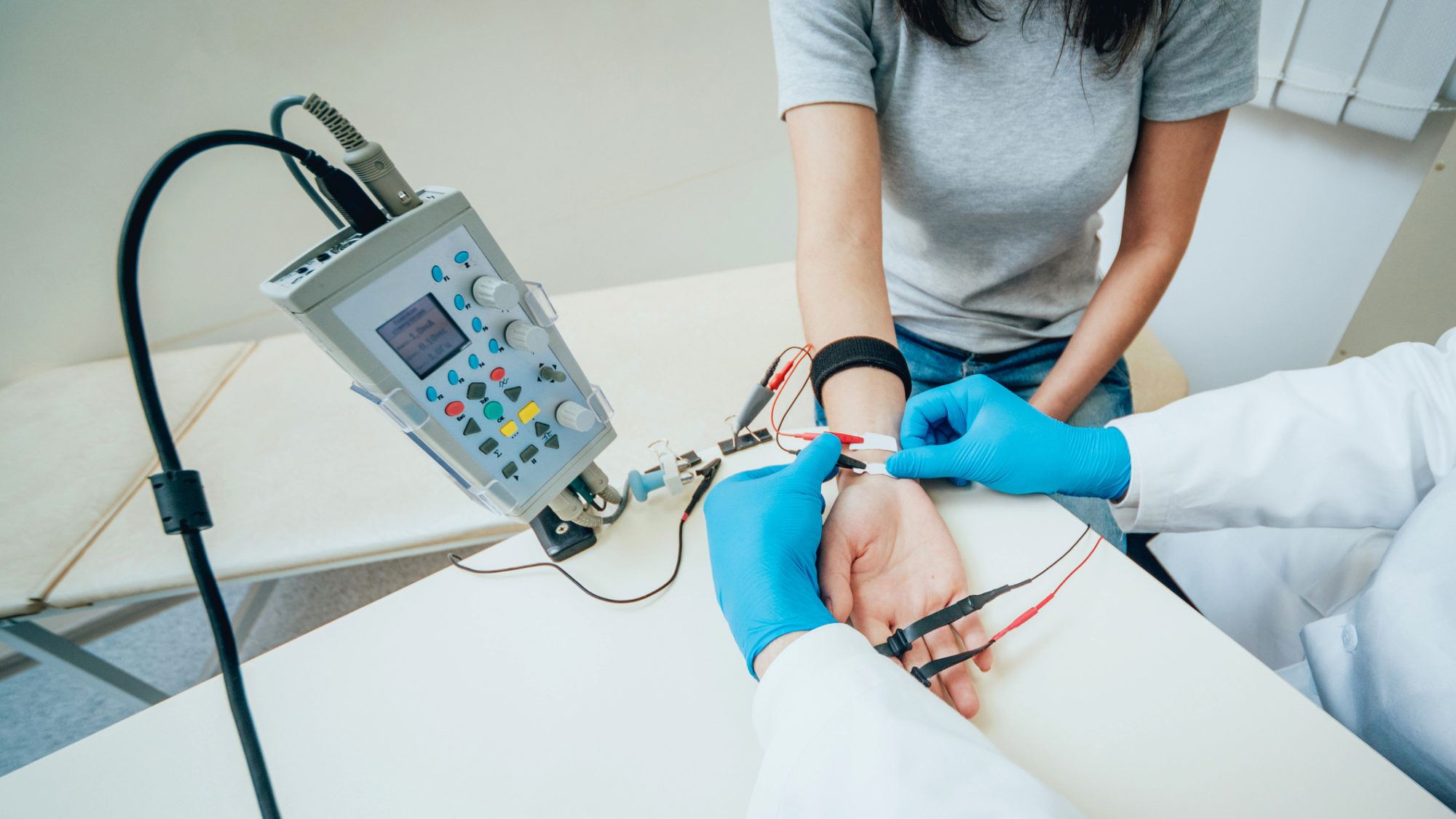
What is Electromyography (EMG) used for?
Electromyography may help diagnose or rule out several conditions that affect nerves or muscles, including:
- Muscular dystrophy
- Myositis
- Myasthenia gravis
- Peripheral neuropathies
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Herniated disc
Am I a good candidate for Electromyography (EMG)?
You may be a good candidate for electromyography if you are having symptoms that could indicate a nerve or muscle disorder, such as weakness, pain, or abnormal sensations. You may feel some discomfort when the needle electrodes are inserted, but complications resulting from an EMG are rare.



